Containers
Containers are useful to create a collection of values. Four kinds of native containers exist in Drift: arrays, lists, sets and dictionaries. Each container has its own properties and logic.
Containers are based on Kotlin types.
For example, Dictionaries are based on Kotlin's Map type.
Arrays
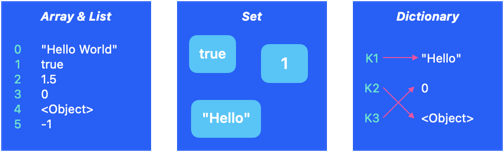
Arrays are useful to store values following an order. Order is defined by integer keys. Array's keys always begin with 0. Without an explicit type, an array can store all types.
Arrays have immutable size.
At this moment, Drift does not implement Arrays.
let anArray: Type[Size] = [ ... ]
Without explicit typing, the [ ... ] expression
is cast as List.
Lists
Lists are useful to store values following an order. Order is defined by integer keys. List's keys always begin with 0. Without an explicit type, a list can store all types.
Lists have mutable size, it is more powerful for content editing than Arrays.
At this moment, Drift does not implement explicit list typing.
let aList: [Type] = [ ... ]
Without explicit typing, the [ ... ] expression
is cast as List.
Sets
Sets get their power from their simplicity. Contrary to Arrays and Lists, Sets permit storing without an order and duplicate values.
At this moment, Drift does not implement Sets.
let aSet: Type[&] = [ ... ]
Without explicit typing, the [ ... ] expression
is cast as List.
Dictionaries
Dictionaries permit storing values by assigning them a unique custom key. Useful to create key-based structures like configurations or objects.
At this moment, Drift does not implement Dictionaries.
let aDict: [KeyType -> ValueType] = [ Key -> Value, ... ]
Without explicit typing, the empty [] expression
is cast as List.